Analyzing Patient Data
Last updated on 2023-09-19 | Edit this page
Estimated time 60 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How can I process tabular data files in Python?
Objectives
- Explain what a library is and what libraries are used for.
- Import a Python library and use the functions it contains.
- Read tabular data from a file into a program.
- Select individual values and subsections from data.
- Perform operations on arrays of data.
Words are useful, but what’s more useful are the sentences and stories we build with them. Similarly, while a lot of powerful, general tools are built into Python, specialized tools built up from these basic units live in libraries that can be called upon when needed.
Loading data into Python
To begin processing the clinical trial inflammation data, we need to load it into Python. We can do that using a library called NumPy, which stands for Numerical Python. In general, you should use this library when you want to do fancy things with lots of numbers, especially if you have matrices or arrays. To tell Python that we’d like to start using NumPy, we need to import it:
PYTHON
import numpyImporting a library is like getting a piece of lab equipment out of a storage locker and setting it up on the bench. Libraries provide additional functionality to the basic Python package, much like a new piece of equipment adds functionality to a lab space. Just like in the lab, importing too many libraries can sometimes complicate and slow down your programs - so we only import what we need for each program.
Once we’ve imported the library, we can ask the library to read our data file for us:
PYTHON
numpy.loadtxt(fname='inflammation-01.csv', delimiter=',')OUTPUT
array([[ 0., 0., 1., ..., 3., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 2., ..., 1., 0., 1.],
[ 0., 1., 1., ..., 2., 1., 1.],
...,
[ 0., 1., 1., ..., 1., 1., 1.],
[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 2., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1., ..., 1., 1., 0.]])The expression numpy.loadtxt(...) is a function call that asks Python
to run the function
loadtxt which belongs to the numpy library.
The dot notation in Python is used most of all as an object
attribute/property specifier or for invoking its method.
object.property will give you the object.property value,
object_name.method() will invoke on object_name method.
As an example, John Smith is the John that belongs to the Smith
family. We could use the dot notation to write his name
smith.john, just as loadtxt is a function that
belongs to the numpy library.
numpy.loadtxt has two parameters: the name of the file we
want to read and the delimiter
that separates values on a line. These both need to be character strings
(or strings for short), so we put
them in quotes.
Since we haven’t told it to do anything else with the function’s
output, the notebook displays it.
In this case, that output is the data we just loaded. By default, only a
few rows and columns are shown (with ... to omit elements
when displaying big arrays). Note that, to save space when displaying
NumPy arrays, Python does not show us trailing zeros, so
1.0 becomes 1..
Our call to numpy.loadtxt read our file but didn’t save
the data in memory. To do that, we need to assign the array to a
variable. In a similar manner to how we assign a single value to a
variable, we can also assign an array of values to a variable using the
same syntax. Let’s re-run numpy.loadtxt and save the
returned data:
PYTHON
data = numpy.loadtxt(fname='inflammation-01.csv', delimiter=',')This statement doesn’t produce any output because we’ve assigned the
output to the variable data. If we want to check that the
data have been loaded, we can print the variable’s value:
PYTHON
print(data)OUTPUT
[[ 0. 0. 1. ..., 3. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 1. 2. ..., 1. 0. 1.]
[ 0. 1. 1. ..., 2. 1. 1.]
...,
[ 0. 1. 1. ..., 1. 1. 1.]
[ 0. 0. 0. ..., 0. 2. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 1. ..., 1. 1. 0.]]Now that the data are in memory, we can manipulate them. First, let’s
ask what type of thing
data refers to:
PYTHON
print(type(data))OUTPUT
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>The output tells us that data currently refers to an
N-dimensional array, the functionality for which is provided by the
NumPy library. These data correspond to arthritis patients’
inflammation. The rows are the individual patients, and the columns are
their daily inflammation measurements.
Data Type
A Numpy array contains one or more elements of the same type. The
type function will only tell you that a variable is a NumPy
array but won’t tell you the type of thing inside the array. We can find
out the type of the data contained in the NumPy array.
PYTHON
print(data.dtype)OUTPUT
float64This tells us that the NumPy array’s elements are floating-point numbers.
With the following command, we can see the array’s shape:
PYTHON
print(data.shape)OUTPUT
(60, 40)The output tells us that the data array variable
contains 60 rows and 40 columns. When we created the variable
data to store our arthritis data, we did not only create
the array; we also created information about the array, called members or attributes. This extra
information describes data in the same way an adjective
describes a noun. data.shape is an attribute of
data which describes the dimensions of data.
We use the same dotted notation for the attributes of variables that we
use for the functions in libraries because they have the same
part-and-whole relationship.
If we want to get a single number from the array, we must provide an index in square brackets after the variable name, just as we do in math when referring to an element of a matrix. Our inflammation data has two dimensions, so we will need to use two indices to refer to one specific value:
PYTHON
print('first value in data:', data[0, 0])OUTPUT
first value in data: 0.0PYTHON
print('middle value in data:', data[29, 19])OUTPUT
middle value in data: 16.0The expression data[29, 19] accesses the element at row
30, column 20. While this expression may not surprise you,
data[0, 0] might. Programming languages like Fortran,
MATLAB and R start counting at 1 because that’s what human beings have
done for thousands of years. Languages in the C family (including C++,
Java, Perl, and Python) count from 0 because it represents an offset
from the first value in the array (the second value is offset by one
index from the first value). This is closer to the way that computers
represent arrays (if you are interested in the historical reasons behind
counting indices from zero, you can read Mike
Hoye’s blog post). As a result, if we have an M×N array in Python,
its indices go from 0 to M-1 on the first axis and 0 to N-1 on the
second. It takes a bit of getting used to, but one way to remember the
rule is that the index is how many steps we have to take from the start
to get the item we want.
In the Corner
What may also surprise you is that when Python displays an array, it
shows the element with index [0, 0] in the upper left
corner rather than the lower left. This is consistent with the way
mathematicians draw matrices but different from the Cartesian
coordinates. The indices are (row, column) instead of (column, row) for
the same reason, which can be confusing when plotting data.
Slicing data
An index like [30, 20] selects a single element of an
array, but we can select whole sections as well. For example, we can
select the first ten days (columns) of values for the first four
patients (rows) like this:
PYTHON
print(data[0:4, 0:10])OUTPUT
[[ 0. 0. 1. 3. 1. 2. 4. 7. 8. 3.]
[ 0. 1. 2. 1. 2. 1. 3. 2. 2. 6.]
[ 0. 1. 1. 3. 3. 2. 6. 2. 5. 9.]
[ 0. 0. 2. 0. 4. 2. 2. 1. 6. 7.]]The slice 0:4 means,
“Start at index 0 and go up to, but not including, index 4”. Again, the
up-to-but-not-including takes a bit of getting used to, but the rule is
that the difference between the upper and lower bounds is the number of
values in the slice.
We don’t have to start slices at 0:
PYTHON
print(data[5:10, 0:10])OUTPUT
[[ 0. 0. 1. 2. 2. 4. 2. 1. 6. 4.]
[ 0. 0. 2. 2. 4. 2. 2. 5. 5. 8.]
[ 0. 0. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 5. 3.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 3. 1. 5. 6. 5. 5. 8.]
[ 0. 1. 1. 2. 1. 3. 5. 3. 5. 8.]]We also don’t have to include the upper and lower bound on the slice. If we don’t include the lower bound, Python uses 0 by default; if we don’t include the upper, the slice runs to the end of the axis, and if we don’t include either (i.e., if we use ‘:’ on its own), the slice includes everything:
PYTHON
small = data[:3, 36:]
print('small is:')
print(small)The above example selects rows 0 through 2 and columns 36 through to the end of the array.
OUTPUT
small is:
[[ 2. 3. 0. 0.]
[ 1. 1. 0. 1.]
[ 2. 2. 1. 1.]]Analyzing data
NumPy has several useful functions that take an array as input to
perform operations on its values. If we want to find the average
inflammation for all patients on all days, for example, we can ask NumPy
to compute data’s mean value:
PYTHON
print(numpy.mean(data))OUTPUT
6.14875mean is a function
that takes an array as an argument.
Not All Functions Have Input
Generally, a function uses inputs to produce outputs. However, some functions produce outputs without needing any input. For example, checking the current time doesn’t require any input.
PYTHON
import time
print(time.ctime())OUTPUT
Sat Mar 26 13:07:33 2016For functions that don’t take in any arguments, we still need
parentheses (()) to tell Python to go and do something for
us.
Let’s use three other NumPy functions to get some descriptive values about the dataset. We’ll also use multiple assignment, a convenient Python feature that will enable us to do this all in one line.
PYTHON
maxval, minval, stdval = numpy.amax(data), numpy.amin(data), numpy.std(data)
print('maximum inflammation:', maxval)
print('minimum inflammation:', minval)
print('standard deviation:', stdval)Here we’ve assigned the return value from
numpy.amax(data) to the variable maxval, the
value from numpy.amin(data) to minval, and so
on.
OUTPUT
maximum inflammation: 20.0
minimum inflammation: 0.0
standard deviation: 4.61383319712Mystery Functions in IPython
How did we know what functions NumPy has and how to use them? If you
are working in IPython or in a Jupyter Notebook, there is an easy way to
find out. If you type the name of something followed by a dot, then you
can use tab completion
(e.g. type numpy. and then press Tab) to see a
list of all functions and attributes that you can use. After selecting
one, you can also add a question mark
(e.g. numpy.cumprod?), and IPython will return an
explanation of the method! This is the same as doing
help(numpy.cumprod). Similarly, if you are using the “plain
vanilla” Python interpreter, you can type numpy. and press
the Tab key twice for a listing of what is available. You can
then use the help() function to see an explanation of the
function you’re interested in, for example:
help(numpy.cumprod).
When analyzing data, though, we often want to look at variations in statistical values, such as the maximum inflammation per patient or the average inflammation per day. One way to do this is to create a new temporary array of the data we want, then ask it to do the calculation:
PYTHON
patient_0 = data[0, :] # 0 on the first axis (rows), everything on the second (columns)
print('maximum inflammation for patient 0:', numpy.amax(patient_0))OUTPUT
maximum inflammation for patient 0: 18.0We don’t actually need to store the row in a variable of its own. Instead, we can combine the selection and the function call:
PYTHON
print('maximum inflammation for patient 2:', numpy.amax(data[2, :]))OUTPUT
maximum inflammation for patient 2: 19.0What if we need the maximum inflammation for each patient over all days (as in the next diagram on the left) or the average for each day (as in the diagram on the right)? As the diagram below shows, we want to perform the operation across an axis:
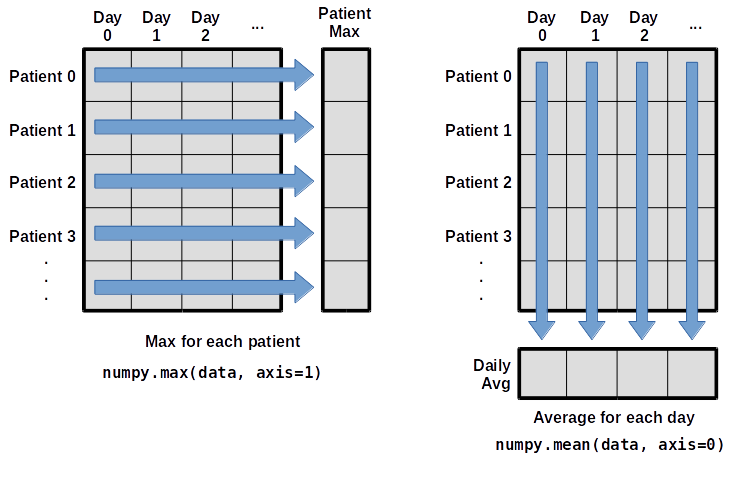
To support this functionality, most array functions allow us to specify the axis we want to work on. If we ask for the average across axis 0 (rows in our 2D example), we get:
PYTHON
print(numpy.mean(data, axis=0))OUTPUT
[ 0. 0.45 1.11666667 1.75 2.43333333 3.15
3.8 3.88333333 5.23333333 5.51666667 5.95 5.9
8.35 7.73333333 8.36666667 9.5 9.58333333
10.63333333 11.56666667 12.35 13.25 11.96666667
11.03333333 10.16666667 10. 8.66666667 9.15 7.25
7.33333333 6.58333333 6.06666667 5.95 5.11666667 3.6
3.3 3.56666667 2.48333333 1.5 1.13333333
0.56666667]As a quick check, we can ask this array what its shape is:
PYTHON
print(numpy.mean(data, axis=0).shape)OUTPUT
(40,)The expression (40,) tells us we have an N×1 vector, so
this is the average inflammation per day for all patients. If we average
across axis 1 (columns in our 2D example), we get:
PYTHON
print(numpy.mean(data, axis=1))OUTPUT
[ 5.45 5.425 6.1 5.9 5.55 6.225 5.975 6.65 6.625 6.525
6.775 5.8 6.225 5.75 5.225 6.3 6.55 5.7 5.85 6.55
5.775 5.825 6.175 6.1 5.8 6.425 6.05 6.025 6.175 6.55
6.175 6.35 6.725 6.125 7.075 5.725 5.925 6.15 6.075 5.75
5.975 5.725 6.3 5.9 6.75 5.925 7.225 6.15 5.95 6.275 5.7
6.1 6.825 5.975 6.725 5.7 6.25 6.4 7.05 5.9 ]which is the average inflammation per patient across all days.
Slicing Strings
A section of an array is called a slice. We can take slices of character strings as well:
PYTHON
element = 'oxygen'
print('first three characters:', element[0:3])
print('last three characters:', element[3:6])OUTPUT
first three characters: oxy
last three characters: genWhat is the value of element[:4]? What about
element[4:]? Or element[:]?
OUTPUT
oxyg
en
oxygenOUTPUT
n
eCreates a substring from index 1 up to (not including) the final index, effectively removing the first and last letters from ‘oxygen’
PYTHON
element = 'oxygen'
print('last three characters:', element[-3:])
element = 'carpentry'
print('last three characters:', element[-3:])
element = 'clone'
print('last three characters:', element[-3:])
element = 'hi'
print('last three characters:', element[-3:])OUTPUT
last three characters: gen
last three characters: try
last three characters: one
last three characters: hiThin Slices
The expression element[3:3] produces an empty string, i.e., a string that
contains no characters. If data holds our array of patient
data, what does data[3:3, 4:4] produce? What about
data[3:3, :]?
OUTPUT
array([], shape=(0, 0), dtype=float64)
array([], shape=(0, 40), dtype=float64)Stacking Arrays
Arrays can be concatenated and stacked on top of one another, using
NumPy’s vstack and hstack functions for
vertical and horizontal stacking, respectively.
PYTHON
import numpy
A = numpy.array([[1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7, 8, 9]])
print('A = ')
print(A)
B = numpy.hstack([A, A])
print('B = ')
print(B)
C = numpy.vstack([A, A])
print('C = ')
print(C)OUTPUT
A =
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]]
B =
[[1 2 3 1 2 3]
[4 5 6 4 5 6]
[7 8 9 7 8 9]]
C =
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]
[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]]Write some additional code that slices the first and last columns of
A, and stacks them into a 3x2 array. Make sure to
print the results to verify your solution.
A ‘gotcha’ with array indexing is that singleton dimensions are
dropped by default. That means A[:, 0] is a one dimensional
array, which won’t stack as desired. To preserve singleton dimensions,
the index itself can be a slice or array. For example,
A[:, :1] returns a two dimensional array with one singleton
dimension (i.e. a column vector).
PYTHON
D = numpy.hstack((A[:, :1], A[:, -1:]))
print('D = ')
print(D)OUTPUT
D =
[[1 3]
[4 6]
[7 9]]An alternative way to achieve the same result is to use Numpy’s delete function to remove the second column of A. If you’re not sure what the parameters of numpy.delete mean, use the help files.
PYTHON
D = numpy.delete(arr=A, obj=1, axis=1)
print('D = ')
print(D)OUTPUT
D =
[[1 3]
[4 6]
[7 9]]Change In Inflammation
The patient data is longitudinal in the sense that each row represents a series of observations relating to one individual. This means that the change in inflammation over time is a meaningful concept. Let’s find out how to calculate changes in the data contained in an array with NumPy.
The numpy.diff() function takes an array and returns the
differences between two successive values. Let’s use it to examine the
changes each day across the first week of patient 3 from our
inflammation dataset.
PYTHON
patient3_week1 = data[3, :7]
print(patient3_week1)OUTPUT
[0. 0. 2. 0. 4. 2. 2.]Calling numpy.diff(patient3_week1) would do the
following calculations
PYTHON
[ 0 - 0, 2 - 0, 0 - 2, 4 - 0, 2 - 4, 2 - 2 ]and return the 6 difference values in a new array.
PYTHON
numpy.diff(patient3_week1)OUTPUT
array([ 0., 2., -2., 4., -2., 0.])Note that the array of differences is shorter by one element (length 6).
When calling numpy.diff with a multi-dimensional array,
an axis argument may be passed to the function to specify
which axis to process. When applying numpy.diff to our 2D
inflammation array data, which axis would we specify?
Since the row axis (0) is patients, it does not make sense to get the difference between two arbitrary patients. The column axis (1) is in days, so the difference is the change in inflammation – a meaningful concept.
PYTHON
numpy.diff(data, axis=1)The shape will be (60, 39) because there is one fewer
difference between columns than there are columns in the data.
By using the numpy.amax() function after you apply the
numpy.diff() function, you will get the largest difference
between days.
PYTHON
numpy.amax(numpy.diff(data, axis=1), axis=1)PYTHON
array([ 7., 12., 11., 10., 11., 13., 10., 8., 10., 10., 7.,
7., 13., 7., 10., 10., 8., 10., 9., 10., 13., 7.,
12., 9., 12., 11., 10., 10., 7., 10., 11., 10., 8.,
11., 12., 10., 9., 10., 13., 10., 7., 7., 10., 13.,
12., 8., 8., 10., 10., 9., 8., 13., 10., 7., 10.,
8., 12., 10., 7., 12.])If inflammation values decrease along an axis, then the
difference from one element to the next will be negative. If you are
interested in the magnitude of the change and not the
direction, the numpy.absolute() function will provide
that.
Notice the difference if you get the largest absolute difference between readings.
PYTHON
numpy.amax(numpy.absolute(numpy.diff(data, axis=1)), axis=1)PYTHON
array([ 12., 14., 11., 13., 11., 13., 10., 12., 10., 10., 10.,
12., 13., 10., 11., 10., 12., 13., 9., 10., 13., 9.,
12., 9., 12., 11., 10., 13., 9., 13., 11., 11., 8.,
11., 12., 13., 9., 10., 13., 11., 11., 13., 11., 13.,
13., 10., 9., 10., 10., 9., 9., 13., 10., 9., 10.,
11., 13., 10., 10., 12.])Keypoints
- Import a library into a program using
import libraryname. - Use the
numpylibrary to work with arrays in Python. - The expression
array.shapegives the shape of an array. - Use
array[x, y]to select a single element from a 2D array. - Array indices start at 0, not 1.
- Use
low:highto specify aslicethat includes the indices fromlowtohigh-1. - Use
# some kind of explanationto add comments to programs. - Use
numpy.mean(array),numpy.amax(array), andnumpy.amin(array)to calculate simple statistics. - Use
numpy.mean(array, axis=0)ornumpy.mean(array, axis=1)to calculate statistics across the specified axis.
